What is the definition of gravitational force?
You probably have an idea of what gravity is, but did you know that you, right now, are actually pulling on every other object in the universe? Find out more about the gravitational force and learn an equation to calculate its pull on other objects. Click next lesson whenever you finish a lesson and…
Definition of gravitational attraction
The only thing one needs to do is observe the interaction of particles, such as gravitational attraction.All mass exerts and experiences gravity and, in space, the gravitational attraction even between masses of modest size can significantly affect their motion.Within a given region, the change in mass…
Gravitational constants
Physicists have used the quantum nature of matter to obtain a highly precise value for the universal gravitational constant, the big G that appears in Isaac Newton s law of how gravity pulls together everything, from planets to apples. Although the technique still needs refinements, physicists believe that in the future it will beat the precision of conventional methods —…
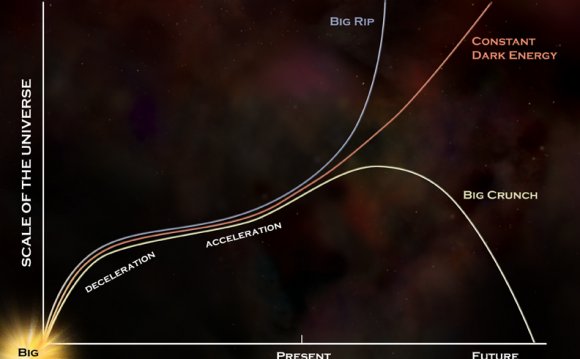
Continue ReadingDark energy in the universe
The galaxy cluster Abell 1689 is famous for the way it bends light in a phenomenon called gravitational lensing. Study of the cluster has revealed secrets about how dark energy shapes the universe. Credit: NASA, ESA, E. Jullo (JPL/LAM), P. Natarajan (Yale) and J-P. Kneib (LAM) A mysterious quantity known as dark energy makes up nearly three-fourths of the universe, yet scientists…
Continue ReadingSurface gravity Earth
Does the moon have significantly different gravity depending on
Continue ReadingLaws VS theories
This article needs attention from an expert in International law . Please add a reason or a talk parameter to this template to explain the issue with the article. WikiProject International law (or its Portal) may be able to help recruit an expert. International legal theory comprises a variety of theoretical and methodological approaches used to explain and analyse the content…
Continue ReadingLaw of Gravitation Physics
Gravity is the weakest of the four fundamental forces, yet it is the dominant force in the universe for shaping the large scale structure of galaxies, stars, etc. The gravitational force between two masses m1 and m2 is given by the relationship: This is often called the universal law of gravitation and G the universal gravitation constant. It is an example of an inverse square…
Continue Reading