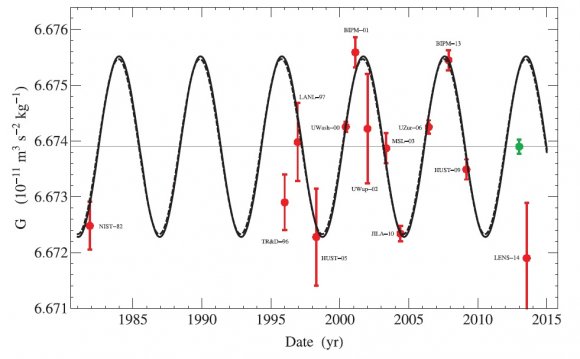
2]/2[pi]c) is the reduced sub-Planckian "action" constant, G is the Newtonian gravitational constant, and c is the velocity of light.j] is a random number in the interval [0, 1], G(t) is the gravitational constant at time t, [M.81 (m/(s^2)) Gravitational constant -32 (ft/(s^2)) Gravitational constant [PI]/(dh)=(MRT)/(dh) Gravitational constant w/m Gravitational constant H E+PV Enthalpy E/v Planck's constant E/f Planck's constant (E[lambda])/c Planck's constant =wavelength; c=speed of light] mv[lambda] Planck's constant =wavelength] [lambda][rho] Planck's constant [[lambda]=wavelength; [rho]=momentum] 6.b] is the bulk density of the powder, and g is equal to the gravitational constant.Gravitational constant G is considered as a linear decreasing functionThe underlying measurements for the mass and density of the planets are based on a single assumption that the equation for gravity is correct and the gravitational constant is universal.The point at which a stellar object can no longer escape being swallowed by a black hole is known as the Schwarzschild radius, a quantity whose value depends on the black hole's mass, the speed of light and the gravitational constant.c], [gamma], T, and p denote the gravitational potential, gravitational constant, thermal conductivity, gas constant, velocity of light, density of ionized component, density of neutral components ([rho] > [[rho].The Planck length is derived from Newton's gravitational constant, the speed of light and Planck's own constant from quantum theory.where v is the angular speed of a test particle about a body of mass M, G is the gravitational constant and r is the distance between the test particle and the massive body, a is a coefficient of the order of unity that depends on the exact definitions of v and r, as well as the geometry of the system.where r is the scalar curvature at any point of the space time and K is the gravitational constant [6].In the Einstein's field equations the Gravitational constant G has been introduced via the Newtonian approximation of the Einstein field equation.
Source: www.thefreedictionary.com
INTERESTING VIDEO

Gravitationa Field Strength or the Acceleration Due to Gravity

Gravitational constant

Gravity
 In physics, mass (from Greek μᾶζα "barley cake, lump (of dough)"), more specifically inertial mass, can be defined as a quantitative measure of an object's resistance to the change of its speed. In addition to this, gravitational mass can be described as a measure...
In physics, mass (from Greek μᾶζα "barley cake, lump (of dough)"), more specifically inertial mass, can be defined as a quantitative measure of an object's resistance to the change of its speed. In addition to this, gravitational mass can be described as a measure...